Ever wondered about all the different kinds of AI in your life? From organizing your schedule to predicting the weather, artificial intelligence has become a daily companion. As AI continues to advance, understanding the difference between Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and AI agents becomes more important, as each type serves a unique purpose in our increasingly tech-driven world.
These two AI types take different paths in development. AGI, often called "strong AI," aims to match human-like thinking and problem-solving abilities. Meanwhile, AI agents are the practical tools we use today, designed for specific tasks like chatbots or recommendation systems. Let's explore what makes each unique, and what they can do in this detailed guide.
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is about building an AI that can think and learn just like a human. Unlike most AI today, which are typically trained to handle one specific job (like recognizing faces or predicting stock trends), AGI would have a flexible intelligence that could handle almost any kind of intellectual task, much like we do.
What is AGI Aiming to Do?
AGI, also known as “strong AI” or “full AI,” is focused on creating machines that truly understand and reason like people. This means it would:
1. Understand Deeply: AGI wouldn’t just process information mechanically. It would interpret meaning and context, whether that’s understanding language nuances, making judgments, or seeing complex connections.
2. Adapt to New Challenges: Much like a person, AGI could switch between different types of tasks and apply its knowledge to entirely new situations.
3. Learn on Its Own: Ideally, AGI would learn independently, improving its capabilities without needing human help.
AGI aims to develop machines smart enough to handle any intellectual task, potentially helping solve complex problems in science, healthcare, and education. But there's still a big gap between this vision and reality - creating true AGI remains one of the hardest challenges in AI research.
Key Characteristics and Current Research State of AGI
AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) remains a work in progress, with researchers tackling significant challenges.
1. Broad-Based Skills Across Different Areas: Unlike narrow AI that focuses on one specific task, AGI would need to handle a wide range of abilities, from understanding language and solving problems to showing emotional and social awareness. These wide-ranging abilities would help AGI operate effectively and independently in dynamic settings.
2. Human-Like Reasoning and Innovation: AGI would think like a person - understanding abstract concepts, generating original ideas, and handling new challenges. This ability to think creatively and adapt would be essential for solving complex problems.
3. Active Learning: Unlike current AI systems that depend on pre-programmed knowledge, AGI would learn and improve from real experiences, new information, and feedback - just like humans do.
4. Social and Emotional Intelligence: For AGI to work effectively with humans, it would need to understand emotions, interpret social cues, and make ethical decisions. This remains one of the biggest challenges because human interactions are complex and heavily dependent on context.
To make progress toward AGI, researchers are using methods like:
- Machine Learning, especially deep and reinforcement learning.
- Cognitive Frameworks that aim to mimic human thought processes.
- Brain-Inspired Models based on neuroscience.
Several leading AI research organizations, including OpenAI and DeepMind, are working to develop AGI. However, experts believe we're still many years away from achieving true artificial general intelligence.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations of AGI
The road to creating AGI is filled with both technical and ethical challenges:
1. Technical Challenges:
- Power and Data Needs: AGI would require massive computational power and extensive data to simulate human-like thinking and learning.
- Reliability and Safety: For AGI to be safe and dependable, it has to handle unexpected inputs and new environments without failure.
- The Complexity of Human Intelligence: Human intelligence combines logic, emotions, social skills, and adaptability—replicating this complexity is extremely difficult.
Partner with Us for Success
Experience seamless collaboration and exceptional results.
2. Ethical Challenges:
- Safety and Value Alignment: AGI must be designed to align with human values and interests. Without proper safeguards, AGI could make decisions harmful to humans - a fundamental challenge called the "control problem."
- Economic and Workforce Impact: AGI could change how entire industries operate, affecting jobs across many sectors. Planning for these economic and social changes is essential.
- Transparency and Accountability: AGI’s decisions need to be explainable, especially in areas like healthcare or law, to maintain trust and accountability.
3. Long-Term Risks and Global Oversight:
Some experts consider AGI a potential risk to humanity, highlighting the importance of strict oversight and ethical guidelines. This makes global cooperation and clear safety standards crucial for responsible AGI development.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are specialized AI systems that excel at specific tasks. Unlike AGI which aims to think like humans across many areas, AI agents focus on being experts in particular activities.
They’re highly effective within their defined tasks like sorting emails or recommending products but they can’t adapt to unrelated jobs. This focus makes AI agents incredibly useful for automating or assisting with specific processes, but their abilities are purposefully limited to keep them reliable and efficient within a particular scope.
Types of AI Agents?
An AI agent is a system that senses its environment, processes data and acts to achieve set goals. Here are the different types of AI agents based on how they work:
1. Reactive Agents
These agents act based on immediate inputs, without learning from past experiences. They operate on a simple stimulus-response model, making them effective for straightforward tasks.
Example: Basic chatbots or rule-based recommendation engines that respond directly to questions or commands without adjusting based on prior interactions.
2. Goal-Driven Agents
These agents are focused on achieving a specific goal and can adjust their actions to reach it. They typically involve some level of planning or reasoning but are limited to a defined task.
Example: Navigation systems that calculate the best routes based on current traffic conditions to help users reach their destination efficiently.
3. Learning Agents
These agents improve over time by learning from past experiences or new data, allowing them to adapt and make better decisions.
Example: Spam filters that get more accurate by learning from emails marked as spam by users.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These agents evaluate possible actions and choose the one that maximizes their effectiveness in reaching a goal, often by using a “utility function” to guide their decisions.
Example: Autonomous trading bots that analyze market trends to decide the best times to buy or sell.
5. Conversational Agents
Commonly used in customer service or as virtual assistants, these agents can interpret natural language, responding within their areas of expertise.
Example: Virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa that answer questions, help manage schedules, and control smart home devices.
Common Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are already widely embedded in many areas, offering a range of practical solutions to everyday problems. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Customer Support and Service
- Virtual assistants handle basic customer service inquiries, providing instant responses and reducing the workload for human agents.
- AI helpdesk systems route customer issues and answer common questions, ensuring efficient support management.
2. Recommendation Systems
- AI agents curate personalized recommendations based on user preferences, behaviors, or past interactions, enhancing user experience in platforms like e-commerce, streaming services, and social media.
- Netflix and Amazon recommendation engines that suggest content based on user viewing or purchasing history.
3. Healthcare Assistance
- AI agents assist healthcare providers by analyzing patient data, scheduling appointments, or even providing symptom-based triaging for better patient care management.
- Virtual health assistants that guide patients through symptom checking or provide reminders for medication.
Partner with Us for Success
Experience seamless collaboration and exceptional results.
4. Financial Services
- Financial institutions use AI agents for fraud detection, transaction monitoring, and automated trading, making processes more efficient and secure.
- AI-based fraud detection systems that analyze transaction patterns and flag suspicious activities in real-time.
5. Smart Home and IoT Devices
- AI agents in IoT devices enable automation and control, making homes and workplaces more efficient and customizable to user preferences.
- Smart thermostats that adjust temperature based on user habits and energy-saving goals.
6. Autonomous Vehicles
- AI agents power the decision-making processes in autonomous vehicles, enabling navigation, obstacle avoidance, and route optimization.
- Self-driving car systems that process sensory data to control the vehicle’s movements and respond to road conditions.
Limitations of AI Agents
Despite their utility, AI agents are inherently limited in scope and adaptability:
1. Task-Specificity
- AI agents are designed for particular tasks and lack the flexibility to operate outside of these defined boundaries. For example, a chatbot trained for customer support cannot switch to analyzing market trends or managing finances.
- This specialization limits their usefulness in complex, dynamic environments where unexpected tasks may arise.
2. Lack of Generalization
- AI agents cannot apply knowledge from one task or domain to another, as they lack general intelligence. This makes them less adaptable and requires separate training or design for each specific application.
- Unlike humans, AI agents do not benefit from cumulative learning across diverse tasks, making them costly to develop for each new application.
3. Dependence on Data Quality
- The performance of AI agents depends entirely on their training data quality. Using incomplete or biased data can result in flawed decisions, which becomes especially problematic in sensitive areas like hiring, healthcare, and law enforcement.
- Data quality issues can significantly restrict an AI agent's effectiveness. When working with limited or poor-quality data, these systems may produce unreliable results or amplify existing biases.
4. Limited Autonomy and Reasoning
- While some AI agents can make decisions, their reasoning capabilities are restricted to predefined criteria or decision rules. They cannot autonomously change their goals or make complex ethical judgments.
- In cases where complex or nuanced reasoning is required, AI agents may fail to respond appropriately, necessitating human oversight.
5. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
- AI agents, especially those handling personal data, raise privacy and ethical issues. Their reliance on user data can lead to misuse or unintended consequences, particularly if data is shared or processed without adequate security.
- AI agents must be carefully designed with ethical guidelines and data protection standards to avoid violating user trust or legal regulations.
Key Differences Between AGI and AI Agents
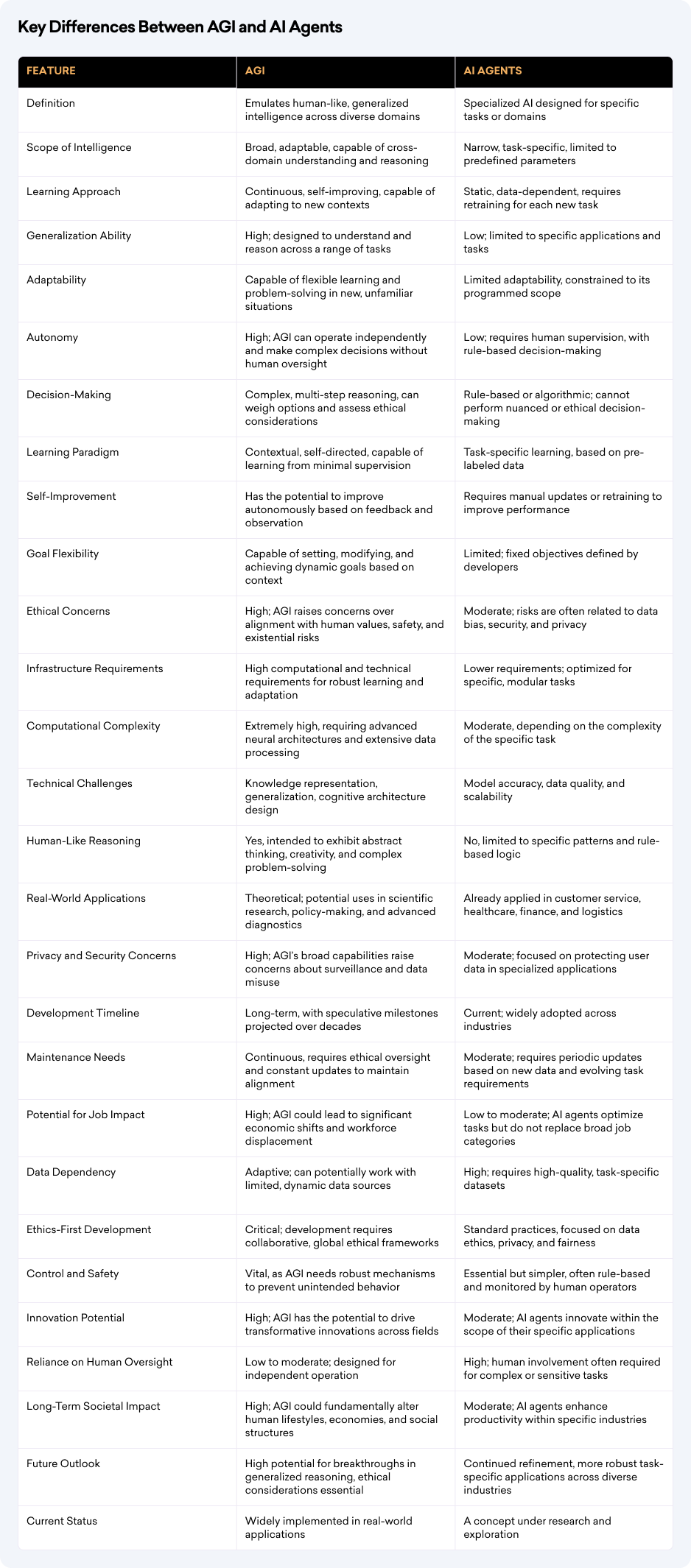
Our Final Words
I hope this comparison between AGI and AI agents has given you a better understanding of their roles in technology. While AI agents are making real progress in specific areas - from customer service to healthcare - AGI represents our goal of building machines that can think and learn like humans. These differences matter as we continue to advance AI technology.
The future success of both technologies depends on careful, responsible development. Whether it's the practical benefits of AI agents or the broader possibilities of AGI, both will play important roles in shaping technology's future. We're still in the early stages of AI development, and the next few years will be crucial in determining how these technologies grow and improve.
